
Global protein production- Forecast 2034 Report
The new OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook for 2025–2034 forecasts moderate and steady growth in global animal product production, signaling a positive trajectory for feed demand over the next decade.
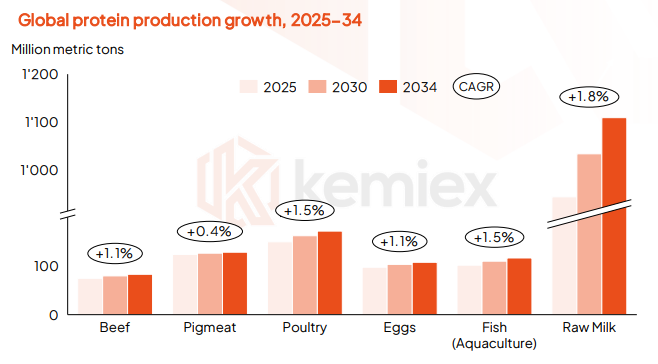
Output of meat is expected to rise given increased breeding efficiency and higher slaughter yields. Within the meat complex, poultry meat production remains dominant, growing at 1.5% annually, underpinned by robust demand, especially in mid-to-high income countries.
Beef production will rise on productivity gains, heavier weights and herd management, while pork production will grow at the slowest rate, just 0.4% p.a., considering challenges like disease pressures and market dynamics.
Milk production will grow the fastest at a 1.8% annual clip. Growth is driven by South East Asian countries, primarily India, despite lower yields. Fish from aquaculture is expected to increase 1.5% annually, heavily concentrated in China, although growth rates are diminishing.
Feed consumption outlook
The projected growth in global animal product production will drive a corresponding increase in feed demand. Kemiex’s proprietary model forecasts global feed consumption will grow at about ~1.5% annually through 2030. A large concentration of feed consumption occurs in China, the U.S. and Europe, however, Latin America, South and East Asian countries are among the core drivers for absolute feed consumption growth over the next five years, fueled by their expanding roles in livestock and aquaculture production.
Latin America, one of the fastest-growing regions for feed consumption, will see demand driven by expanding poultry and pig meat production, while rising dairy and aquaculture output will be key for South Asian countries.
Lower feed costs, driven by a decline in grain and oilseed prices since the 2022 peak, likely support higher feed use. For example, lower soybean meal prices, partially driven by new biofuel plans in U.S. and Brazil, offer a cheap protein source for nutritionists. A prolonged depression in feed prices could impact inclusion rates for amino acids as formulators minimize costs, especially in lower income countries.

Download the full report or get in touch with our team for more information. to receive a copy directly.
Stay ahead of market shifts with data you can trust.